Complete the following table for the three key subatomic particles. – Complete the following table for the three key subatomic particles: electrons, protons, and neutrons. This table will provide a comprehensive overview of the fundamental properties and characteristics of these particles, which are the building blocks of all matter in the universe.
Subatomic particles play a crucial role in determining the chemical and physical properties of elements and compounds. Understanding their properties is essential for comprehending the behavior of matter at the atomic and molecular level.
Subatomic Particle Properties: Complete The Following Table For The Three Key Subatomic Particles.
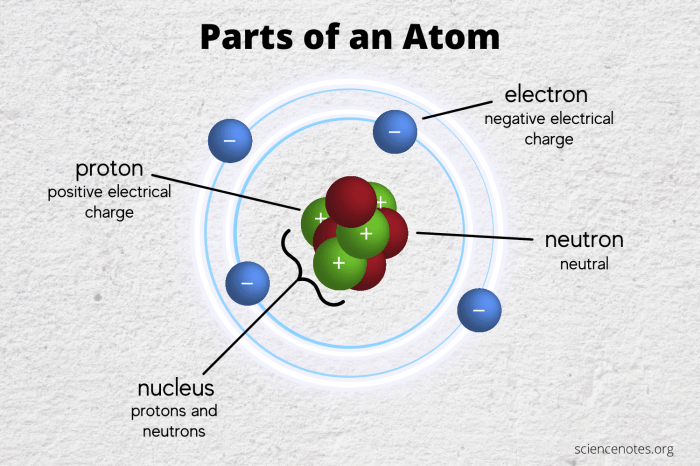
Subatomic particles are the fundamental building blocks of matter. They are extremely small, with masses that are only a fraction of an atomic mass unit (amu). The three main types of subatomic particles are electrons, protons, and neutrons.
| Particle | Charge | Mass (amu) | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electron | -1 | 0.00055 | Outside the nucleus, in energy levels |
| Proton | +1 | 1.0073 | Inside the nucleus |
| Neutron | 0 | 1.0087 | Inside the nucleus |
Electron Characteristics
Electrons are negatively charged particles with a mass of 0.00055 amu. They are located outside the nucleus of an atom, in energy levels. The number of electrons in an atom determines its chemical properties.Electrons play a crucial role in chemical reactions and electrical conductivity.
They are also responsible for the emission of light in certain materials, such as light bulbs and lasers.
Proton Characteristics
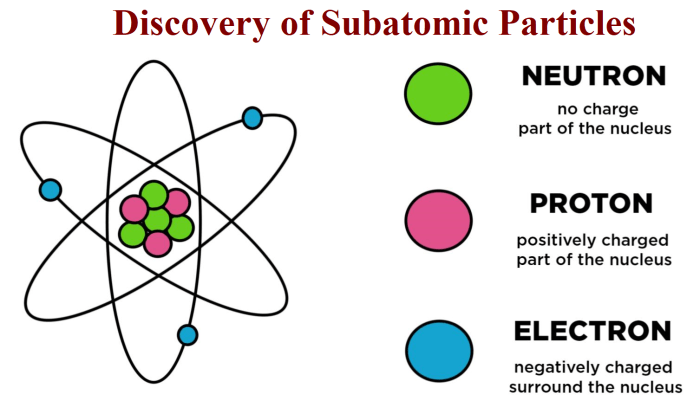
Protons are positively charged particles with a mass of 1.0073 amu. They are located inside the nucleus of an atom, along with neutrons. The number of protons in an atom determines its atomic number and chemical element.Protons are responsible for the strong nuclear force, which holds the nucleus together.
They also play a role in nuclear reactions, such as nuclear fission and fusion.
Neutron Characteristics

Neutrons are neutral particles with a mass of 1.0087 amu. They are located inside the nucleus of an atom, along with protons. The number of neutrons in an atom determines its isotope.Neutrons play a role in the strong nuclear force and help to stabilize the nucleus.
They are also used in neutron radiography, which is a non-destructive testing technique.
Interactions Between Subatomic Particles
Electrons and protons have opposite charges, so they attract each other through electrostatic interactions. These interactions are responsible for the formation of atoms and molecules.Protons and neutrons are both positively charged, but they are held together by the strong nuclear force.
This force is much stronger than the electrostatic force, so it overcomes the repulsion between the protons and keeps the nucleus stable.
Applications of Subatomic Particles
Electrons are used in a wide variety of electronic devices, such as transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits. They are also used in electron microscopes, which can magnify objects up to millions of times.Protons are used in nuclear power plants to generate electricity.
They are also used in particle accelerators, which are used to study the fundamental particles of matter.Neutrons are used in neutron radiography, which is a non-destructive testing technique. They are also used in nuclear reactors to control the fission process.
FAQ Resource
What is the charge of an electron?
Electrons have a negative charge of -1.
What is the mass of a proton?
Protons have a mass of approximately 1 atomic mass unit (amu).
Where are neutrons located within an atom?
Neutrons are located in the nucleus of an atom, along with protons.